I – How Can I change Qnap Ip Adress?
II – Can I combine 2 lan ports for faster data transfer? (Port Trunking, Load Balance & Failover Configuration)
III – Can I Use my Qnap over Wireless Network? (How to Use Wi-Fi Dongle With Qnap)
IV – Can I connect my Qnap NAS from Internet? (DDNS Settings)
V – Which Ports Does Qnap Use?
VI – What is Port Forwarding?
VII – How can I configure Port Forwarding on my Modem?
VIII – How to Change Ip Adress via Command Line? (For Advanced Users!)
IX – How to To Give IP Adress From DHCP via Command Line (For Advanced Users!)
.
I – How Can I change Qnap Ip Adress?
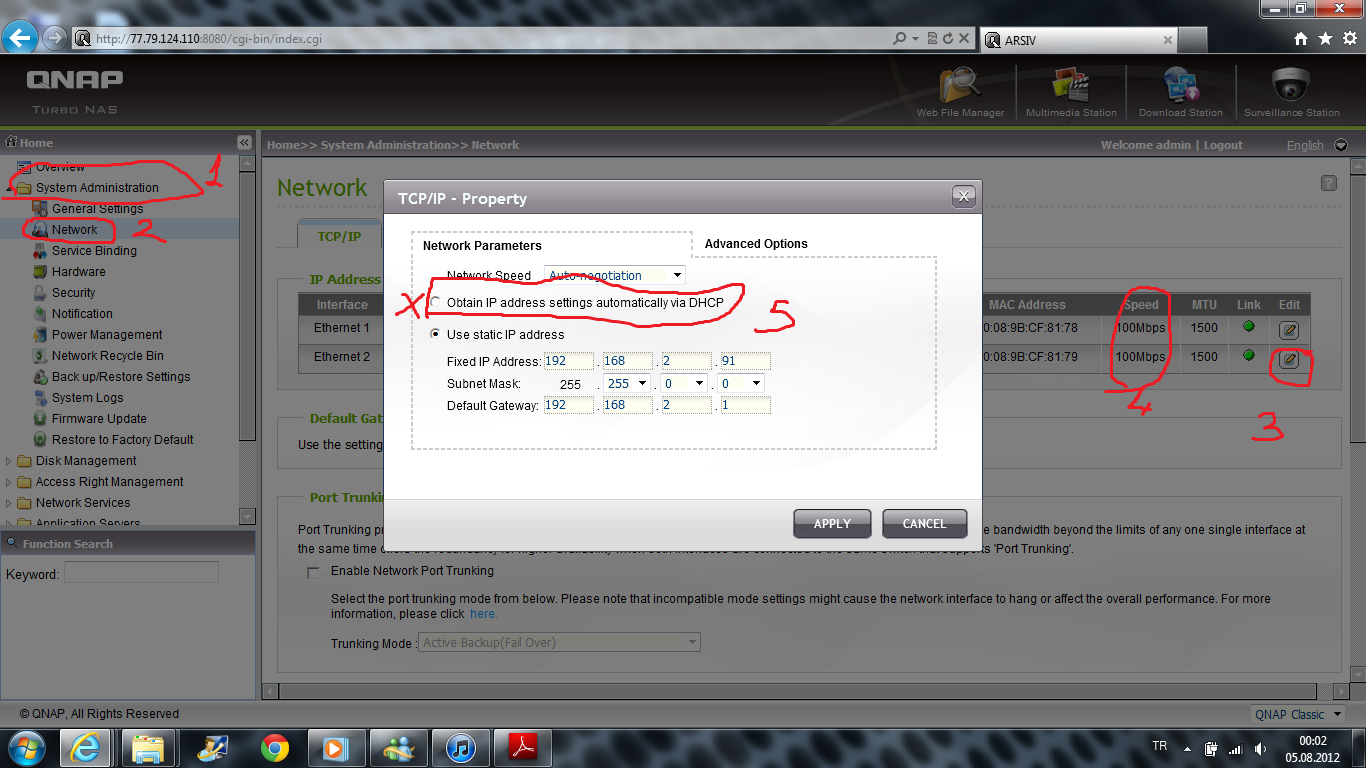
Login Qnap and go to -> System Administration ->Network -> TCP /IP. Press Pencil Icon at the end of “Ethernet 1″ or “Ethernet 2″ to change Qnap IP.
Also, at this picture my network speed seems 100 mbit. If you’r using a Gbit swith, change your Network speed from Auto Negotation to 1000 mbit.
Second way to change is Qnapfinder, but I dont advice this way, because it cost too much time to configure.
What is DHCP server and advice Qnap DHCP server confgiration?
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a network protocol that is used to configure network devices so that they can communicate on an IP network
It gives Qnap IP adress automaticly, but some wrong configured DHCP servers has a chance to give different IP in time, or may cause IP crash on Newtor, so dont use this option. Always give Qnap IP adress manually.
I give Ip adress manually at first Installation setup but Qnap doesnt change this adress and give 169.254.100.100 Ip adress.
At first time setup, Qnap configure first ethernet port Ip configration. Plese check if you plug 1.th or 2.th Lan port. If you swith back to 1.th port, you can reach Qnap which Ip adress you configure.
Can I configure different IP adress to Qnap devices;
Sure, I use my Qnap that way. I plug my first ethernet port to external switch, give a real Ip adress (77.79.124.x) and can use it witout port forwarding. Also plug my second ethernt port to another switch, and give an internal IP adress (192.168.2.91) to my second ethernet port from our internal IP range, and I can use my Qnap without problem.
Can I use Qnap ethernet ports just like Switch to combine my 2 networks?
No, its not possable.
.
II – Port Trunking : Can I Combine 2 lan ports for faster data transfer?
The NAS supports port trunking which combines two Ethernet interfaces into one to increase the bandwidth and offers load balancing and fault tolerance (also known as failover). Load balancing is a feature which distributes the workload evenly across two Ethernet interfaces for higher redundancy. Failover is the capability to switch over to a standby network interface (also known as the slave interface) when the primary network interface (also known as the master interface) does not correspond correctly to maintain high availability.
To use port trunking on the NAS, make sure at least two LAN ports of the NAS have been connected to the same switch and the settings described in sections (i) and (ii) have been configured.
Follow the steps below to configure port trunking on the NAS:
| 1. | Click “Port Trunking“. |
| 2. | Select the network interfaces for a trunking group (Ethernet 1+2, Ethernet 3+4, Ethernet 5+6, or Ethernet 7+8). Choose a port trunking mode from the drop-down menu. The default option is Active Backup (Failover). |
| 3. | Select a port trunking group to use. Click “Apply”. |
| 4. | Click “here” to connect to the login page. |
| 5. | Go to “Control Panel” > “System Settings” > “Network” > “TCP/IP”. |
| 6. | Click the “Edit” button under “Edit” to edit the network settings. |
|
Note:
|
The port trunking options available on the NAS:
|
Field |
Description |
Switch Required |
|
Balance-rr (Round-Robin) |
Round-Robin mode is good for general purpose load balancing between two Ethernet interfaces. This mode transmits packets in sequential order from the first available slave through the last. Balance-rr provides load balancing and fault tolerance. |
Supports statictrunking. Make sure static trunking is enabled on the switch. |
|
Active Backup |
Active Backup uses only one Ethernet interface. It switches to the second Ethernet interface if the first Ethernet interface does not work properly. Only one interface in the bond is active. The bond’s MAC address is only visible externally on one port(network adapter) to avoid confusing the switch. Active Backup mode provides fault tolerance. |
General switches |
|
Balance XOR |
Balance XOR balances traffic by splitting up outgoing packets between the Ethernet interfaces, using the same one for each specific destination when possible. It transmits based on the selected transmit hash policy. The default policy is a simple slave count operating on Layer 2 where the source MAC address is coupled with destination MAC address. Alternate transmit policies may be selected via the xmit_hash_policy option. Balance XOR mode provides load balancing and fault tolerance. |
Supports statictrunking. Make sure static trunking is enabled on the switch. |
|
Broadcast |
Broadcast sends traffic on both network interfaces. This mode provides fault tolerance. |
Supports statictrunking. Make sure static trunking is enabled on the switch. |
|
IEEE 802.3ad (Dynamic Link Aggregation) |
Dynamic Link Aggregation uses a complex algorithm to aggregate adapters by speed and duplex settings. It utilizes all slaves in the active aggregator according to the 802.3ad specification. Dynamic Link Aggregation mode provides load balancing and fault tolerance but requires a switch that supports IEEE 802.3ad with LACP mode properly configured. |
Supports 802.3ad LACP |
|
Balance-tlb (Adaptive Transmit Load Balancing) |
Balance-tlb uses channel bonding that does not require any special switch. The outgoing traffic is distributed according to the current load on each Ethernet interface (computed relative to the speed). Incoming traffic is received by the current Ethernet interface. If the receiving Ethernet interface fails, the other slave takes over the MAC address of the failed receiving slave. Balance-tlb mode provides load balancing and fault tolerance. |
General switches |
|
Balance-alb (Adaptive Load Balancing) |
Balance-alb is similar to balance-tlb but also attempts to redistribute incoming (receive load balancing) for IPV4 traffic. This setup does not require any special switch support or configuration. The receive load balancing is achieved by ARP negotiation sent by the local system on their way out and overwrites the source hardware address with the unique hardware address of one of the Ethernet interfaces in the bond such that different peers use different hardware address for the server. This mode provides load balancing and fault tolerance. |
General switches |
.
III – Can I Use My Qnap Over Wireless Network?
To connect the NAS to a Wi-Fi network, plug in a wireless dongle into a USB port of the NAS. The NAS will detect a list of wireless access points. You can connect the NAS to the Wi-Fi network in two ways.
|
Note:
|
Method 1: Connecting to an existing Wi-Fi network:
A list of Wi-Fi access points with signal strength are displayed on the “Wi-Fi Network Connection” panel.
|
Icon / Option |
Name |
Description |
|
Rescan |
Rescan |
To search for the Wi-Fi networks in range. |
|
|
Secured network |
This icon shows that the Wi-Fi network requires a network key; enter the key to connect to the network. |
|
|
Connect |
To connect to Wi-Fi network. If a security key is required, you will be prompted to enter the key. |
|
|
Edit |
To edit the connection information. You may also select to connect to the Wi-Fi network automatically when it is in range. |
|
|
Disconnect |
To disconnect from the Wi-Fi network. |
|
|
Remove |
To delete the Wi-Fi network profile from the panel. |
|
Show all |
Show all |
Select this option to display all the available Wi-Fi networks. Unselect this option to show only the configured network profiles. |
Click “Rescan” to search for available Wi-Fi networks in range. Select a Wi-Fi network to connect to and click the “Connect” button. Enter the security key if it is a security-key enabled network. Click “Next” and the NAS will attempt to connect to the wireless network. You can view the status of the configured network profiles.
|
Message |
Description |
|
Connected |
The NAS is currently connected to the Wi-Fi network. |
|
Connecting |
The NAS is trying to connect to the Wi-Fi network. |
|
Out of range or hidden SSID |
The wireless signal is not available or the SSID is not broadcast. |
|
Failed to get IP |
The NAS is connected to the Wi-Fi network but could not get an IP address from the DHCP server. Please check the router settings. |
|
Association failed |
The NAS cannot connect to the Wi-Fi network. Please check the router settings. |
|
Incorrect key |
The security key entered is incorrect. |
|
Auto connect |
Automatically connect to the Wi-Fi network if it is in range. The auto connection function is not supported if the SSID of the Wi-Fi network is not broadcast. |
Method 2: Manually connecting to a Wi-Fi network:
To manually connect to a Wi-Fi network that does not broadcast its SSID (network name), click “Connect to a Wi-Fi network”.
You can choose to connect to an ad hoc network in which you can connect to any wireless devices without the need for an access point. To set up, follow the steps below:
| 1. | Enter the network name (SSID) of the wireless network and select the security type. |
| o | No authentication (Open): No security key required. |
| o | WEP: Enter up to 4 WEP keys and choose 1 key to be used for authentication. |
| o | WPA-Personal: Choose either the AES or TKIP encryption type and enter the encryption key. |
| o | WPA2-Personal: Enter a security key. |
| 2. | Type in the security key. |
| 3. | Click “Finish” after the NAS has added the Wi-Fi network. |
| 4. | To edit the IP address settings, click the “Edit” button. You can select to obtain the IP address automatically by DHCP or configure a fixed IP address. |
If the Wi-Fi connection is the only connection between the NAS and the router/AP, you must select “WLAN1″ as the default gateway in “Network” > “TCP/IP” page. Otherwise, the NAS will not be able to connect to the Internet or communicate with another network.
|
Note:
|
.
IV – Can I Use my Qnap NAS Over Internet?
“Stay connected to your NAS from everywhere”
::__IHACKLOG_REMOTE_IMAGE_AUTODOWN_BLOCK__::9
Dynamic Domain Name Service (DDNS) is a service used to map a domain name to the dynamic IP address of a network device. QNAP NAS supports DDNS for quick access to the server on the Internet by an easy-to-remember domain name (URL) instead of a lengthy IP address. Once the IP is changed, the NAS will automatically update the information to the DDNS provide to ensure it is always available for remote access.
1. Register DDNS service
1.1 Domain Name
A domain name is a translation operated by a DNS (Domain Name System) provider to convert an Internet IP address into a name (e.g. ‘74.125.153.104’ is www.google.com).
1.2 Register a free DDNS account
If your NAS is set up to use a dynamic IP address, you may register a free DDNS (dynamic DNS) account from a DNS service provider and assign a unique host name for easy access to your NAS on the Internet.
To register a DDNS account, please refer to the steps below:
Choose a DNS service provider. QNAP NAS currently supports the following DDNS service providers:
- http://www.no-ip.com/
- http://www.dyndns.org/
- http://update.ods.org/
- http://www.dhs.org/
- http://www.dyns.cx/
- http://www.3322.org/
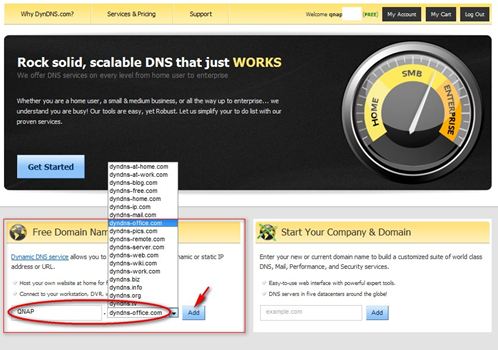
Create an account. Here we take http://www.dyndns.org/ as an example.
Visit http://www.dyndns.org/. Click ‘Sign In’ and ‘Create an Account’ to register a DynDNS account.
 0
0
Complete the form to create your free account.
 1
1
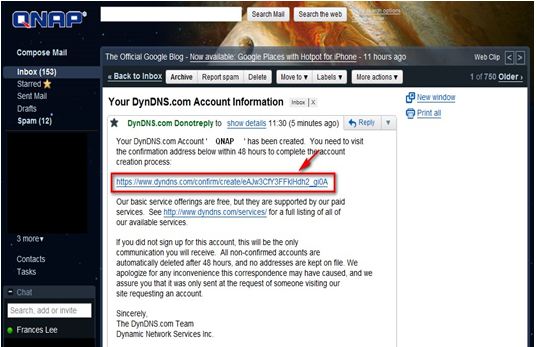
A confirmation email will be sent to your email address.
Click the link in the email for confirmation.
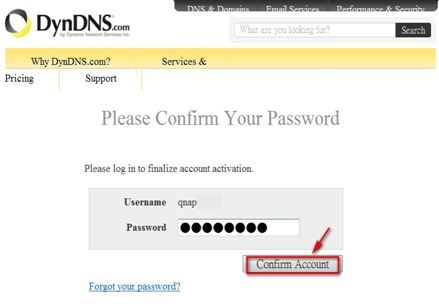
Click ‘Confirm Account’ and login DynDNS.
Register a host name for your NAS. A host name is a unique name that identifies your server. Pick something you will remember. For example, fill in ‘QNAP’ and select ‘dyndns-office.com’. Then click ‘Add’.
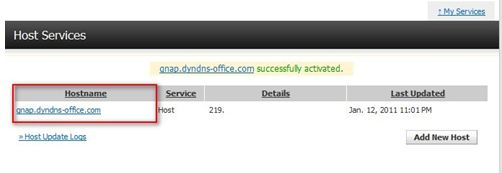
Activate the host name.
Now you can login the NAS and set up the DDNS service.
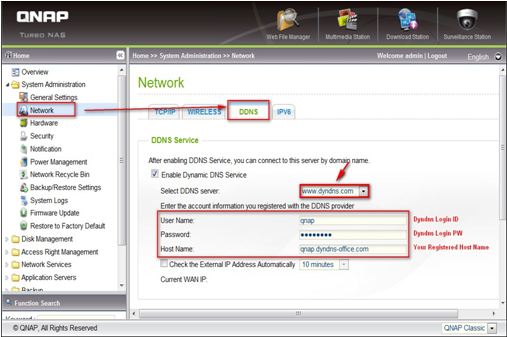
1.3 Configure DDNS service on QNAP NAS
Login your NAS and go to ‘System Administration’ > ‘Network’ > ‘DDNS’. Enter the DDNS information you registered from the DNS service provider. You may also schedule the NAS to update the DDNS record periodically by configuring the ‘Check the External IP Address Automatically’ option.
After finishing the settings, the NAS will start to update the WAN IP to the DDNS provider for domain name mapping. You can now connect to the NAS by the domain name (qnap.dyndns-office.com) on the Internet.
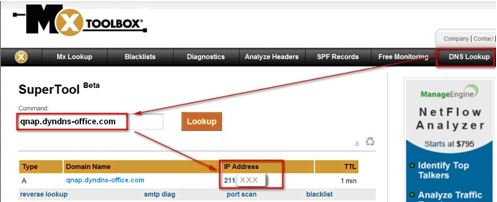
1.4 Lookup for your DNS if you need to verify:
To check that the domain name of the NAS is correctly mapped to its WAN IP, you may visit http://www.mxtoolbox.com/DNSLookup.aspx. Enter your domain name for DNS lookup and it will return your IP address.
2. Port Forwarding
If your NAS is located behind the NAT router, you need to open the port numbers on the router for remote access to the NAS. This function is available on most routers in the market and is often known as “Port Forwarding”, “NAT Server”, or “Virtual Server”. You may select the services with the corresponding port numbers to be opened on the router for Internet access. For example, to access the administration interface of Turbo NAS series, you need to open port 8080.
| NAS Services | Default Port |
|---|---|
| Web-based system management | 8080 |
| FTP | 21 |
| Passive FTP | 55536~56559 |
| Web Server | 80 |
| Download Station (BitTorrent download) | 6881-6999 |
| Remote replication (Rsync) | 873 |
| Telnet | 13131 |
| SSH | 22 |
| SSL | 443 |
| SMTP | 25 |
| Samba | 445 |
| MySQL | 3306 |
| TwonkyMedia | 9000 |
.
VI – Which Ports Does Qnap Use?
| Current open service ports on QNAP NAS | |
| NAS Services | Default Port |
| Web-based system management | 8080 (All models, TS-101/201 with firmware v2.3.0 or later) |
| Web-based system management | 6000 (TS-100/101/201 firmware prior to v2.1.1) |
| FTP | 21 |
| Passive FTP | 55536–56559 |
| Web Server | 80 |
| Download Station (BT download) | 6881–6999 |
| Remote replication (Rsync) | 873 |
| Telnet | 13131 |
| SSH | 22 |
| SSL | 443 |
| SMTP | 25 |
| Samba | 445 |
| MySQL | 3306 |
| TwonkyMedia | 9000 |
.
VI – What is Port Forwarding; (from : http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-port-forwarding.htm)
Port forwarding is the process that your router or firewall uses to sort the right kind of network data to the right port. Computers and routers use ports as a way to organize network data. Different types of data, such as web sites, file downloads, and online games, are each assigned a port number. By using port forwarding, the router or firewall sends the correct data to the correct place.
.
VII – How can I configure Port Forwarding on my Modem?
Taken From : http://www.wikihow.com/Set-up-Port-Forwarding-on-a-Router
Steps
-
1 – Open your router’s admin console by typing the standard IP address for your computer into your web browser’s URL box. For most routers, this will be either 192.168.0.1. or 192.168.1.1. However, if you want to figure out the IP, here’s how to do it:
- For Windows: Open the command prompt and enter ipconfig/all.
- For Mac: Open the command prompt and enter netstat -nr.
- For Linux: Open the command prompt and enter ifconfig wlan0.
-
2 – Enter your username and password. If you’ve already configured the security settings for your router, enter the username and password you chose then. If not, here’s what to do:
- On Linksys routers, type “admin” for both the username and the password.
- On Netgear routers, type “admin” for the username and “password” for the password.
- On other routers, try leaving the username empty and entering “admin” for the password.
-
3
Open the Port Forwarding or Applications and Gaming tab. Each router will be slightly different, but look for these two options. If you don’t see them, try Advanced Settings and look for a Port Forwarding subsection.
-
4 – Enter your desired ports.
- Enter your application name. For a list of which ports an application might use, see the Sources and Citations section below.
- Select the ports you wish to use. If you only want one port open, enter the same number in Start and End. If you wish to open a range of ports (say 5), you might type 3784 in Start and 3788 in End.
- Select Both if you’re asked to choose between TCP and UDP.
-
::__IHACKLOG_REMOTE_IMAGE_AUTODOWN_BLOCK__::2
 The page should look something like this.
The page should look something like this.Enter your IP address. Your router might ask for the whole address, or only the last three digits. If you don’t know it, go back to the Command Prompt and enter ipconfig.
-
5 – Save your settings. You might need to restart your router for them to take effect
Also here is a video How to do;
[pro-player width='530' height='253' type='video']http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_embedded&v=AAAcTQ5PTGg[/pro-player]
.
VIII – How to Change Ip Adress via Command Line? (For Advance User!)
1 – Login Qnap Via SSH;
2 – Type This Commands; (Ex; you want to chagne first ethernet port IP adress 192.168.1.1)
/sbin/setcfg eth0 “Gateway” 192.168.1.1;
/sbin/setcfg eth0 “IP Address” 192.168.1.2;
/etc/init.d/network.sh restart
.
IX – How to To Give IP Adress From DHCP via Command Line ;
Proceed as follows:
- Power off your NAS
- Eject all drives. (Do not remove them, just eject them by 1″ (3cm) so they are no longer connected to the SATA Bus).
- Turn on the NAS. (You’ll hear a short “beep“)
- After 2-3 minutes, a long beep will be heard, and the NAS can be “found” via QNAP QFinder
- Hot-plug all HDDs into the NAS (Do not power off the NAS. Do not follow the Quick Setup prompts)
- Access your NAS via SSH (using PuTTY) (Note: it’s IP address may have changed, use QNAP QFinder if necessary to determine it’s IP address)
- Execute the following commands on the NAS:
config_util 1
storage_boot_init 1
setcfg -f /share/HDA_ROOT/.config/uLinux.conf eth0 'Configure' 'TRUE'
setcfg -f /share/HDA_ROOT/.config/uLinux.conf eth0 'Use DHCP' 'TRUE'
setcfg -f /share/HDA_ROOT/.config/uLinux.conf eth0 'Usage' 'DHCP'
sleep 2
reboot
Qnap Network / IP AyarlarıQnap Netork / IP Settings,







merhabalar, qnap vs 2108 pro+ model nvr cihazıyla uzakda statik ipye bağlı bir kamerayı
bağlayabilirmiyim
Elbetteki, (eğer Qnap’a ve IP kameraya WAN üzerinden ulaşabiliyorsanız tabiki..)
Advanced…
You forgot advanced also means configuring IP via command line.
Who need this kind of informatin??
Type This Commands; (Ex; you want to chagne first ethernet port IP adress 192.168.1.1)
/sbin/setcfg eth0 “Gateway” 192.168.1.1;
/sbin/setcfg eth0 “IP Address” 192.168.1.2;
/etc/init.d/network.sh restart
Merhaba,
QNAP’i mi fabrika ayarlarına aldım. Fakat şimdi erişemiyorum. Default bir statik ip’si var mı ? Yardımcı olabilirseniz sevinirim.
Qnap’ın standart IP adres 169.254.100.100:8080 dir
hi
Can insert the static arp into my qnap ts-439 pro 2? Thanks a lot
Carlo